Assignment 5. ( commands for octave 3.0.1)
Question 1. Octave commands for constructing a 256 by 256 matrix with entries of 0 everywhere except inside a circle with a radius of 50 where the values are 1.
function val = circle(x,y)
> val=zeros(256);
> for i=1:256; for j=1:256;
> if (i-x)^2+(j-y)^2 <=2500; > val(i,j)=1;
> end
> end
> end
> end
> imshow(circle(128,128))
Question 2. Give octave commands to draw the top part of figure 6.4
> P(:,:,1)=circle(156,103);
> P(:,:,2)=circle(113,128);
> P(:,:,3)=circle(156,153);
>imshow(255*P)
Question 3.
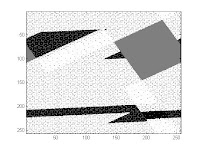
Skewing bigT with s=2.
> bigT = 255*ones(256);
octave-3.0.1.exe:68> bigT(30:79,64:191)=zeros(50,128);
octave-3.0.1.exe:69> bigT(50:199,111:146)= zeros(150,36);
octave-3.0.1.exe:70> Ts = zeros(256);
octave-3.0.1.exe:71> for i=1:256; for j=1:256;
> Ts(i,round(mod(j+2*i,256)+1))=bigT(i,j); end; end;
octave-3.0.1.exe:72> imshow(Ts)

rotating the skewed Ts by 7pi/6
Trot=128*ones(256);
c=cos(7*pi/6)
s=sin(7*pi/6)
for i=1:256; for j=1:256;
Trot(round(mod(i*c-j*s,256)+1),round(mod(i*s+j*c,256)+1))=Ts(i,j);
end
end
imshow(Trot)
Question 1. Octave commands for constructing a 256 by 256 matrix with entries of 0 everywhere except inside a circle with a radius of 50 where the values are 1.
function val = circle(x,y)
> val=zeros(256);
> for i=1:256; for j=1:256;
> if (i-x)^2+(j-y)^2 <=2500; > val(i,j)=1;
> end
> end
> end
> end
> imshow(circle(128,128))
Question 2. Give octave commands to draw the top part of figure 6.4
> P(:,:,1)=circle(156,103);
> P(:,:,2)=circle(113,128);
> P(:,:,3)=circle(156,153);
>imshow(255*P)
Question 3.
Skewing bigT with s=2.
> bigT = 255*ones(256);
octave-3.0.1.exe:68> bigT(30:79,64:191)=zeros(50,128);
octave-3.0.1.exe:69> bigT(50:199,111:146)= zeros(150,36);
octave-3.0.1.exe:70> Ts = zeros(256);
octave-3.0.1.exe:71> for i=1:256; for j=1:256;
> Ts(i,round(mod(j+2*i,256)+1))=bigT(i,j); end; end;
octave-3.0.1.exe:72> imshow(Ts)

rotating the skewed Ts by 7pi/6
Trot=128*ones(256);
c=cos(7*pi/6)
s=sin(7*pi/6)
for i=1:256; for j=1:256;
Trot(round(mod(i*c-j*s,256)+1),round(mod(i*s+j*c,256)+1))=Ts(i,j);
end
end
imshow(Trot)


 Above is the graph for wavelength versus y. It represents the wavelengths for different saturations of green.
Above is the graph for wavelength versus y. It represents the wavelengths for different saturations of green.
-yellow.jpg) Yellow component of the image in problem 6.6 as it would appear on monochrome monitor.
Yellow component of the image in problem 6.6 as it would appear on monochrome monitor.-magenta.jpg) Magenta component of the image in problem 6.6 as it would appear on monochrome monitor.
Magenta component of the image in problem 6.6 as it would appear on monochrome monitor.-cyan.jpg)
CMYfedintoRGB.jpg)

